Voice Communication App with Agora
About Voice Communication
Voice and video chat can be added to many products to make them collaborative and interactive.
There are many communications SDK providers such as Agora, Dolby.io, Tokbox, Twilio, Amazon Chime, and plain old webRTC. But if your app has more complex audio features, you may want to connect your communications service to Switchboard so that you can manage your audio graph more easily.
Projects with multiple audio features quickly become unwieldy and would otherwise require lots of custom glue code. We built this sample app to show you how to quickly connect a voice communication service to the Switchboard SDK.
In this example we will create an app for real-time voice communication over the internet, with the ability to communicate with multiple people in the same virtual room.
Voice Communication App
You can find the source code on the following link:
Voice Communication App - iOS
You can find the source code on the following link:
Voice Communication App - Android
The app has the following features:
- Two-way voice communication with multiple users in a room
- Ability to enter custom username
- Ability to join an arbitrarily-named room
- User presence in a list form
It consists of the following single screen:
- Room Screen: Voice communication in a room, custom username and room name setting, user presence list
This example uses the Agora Extension.
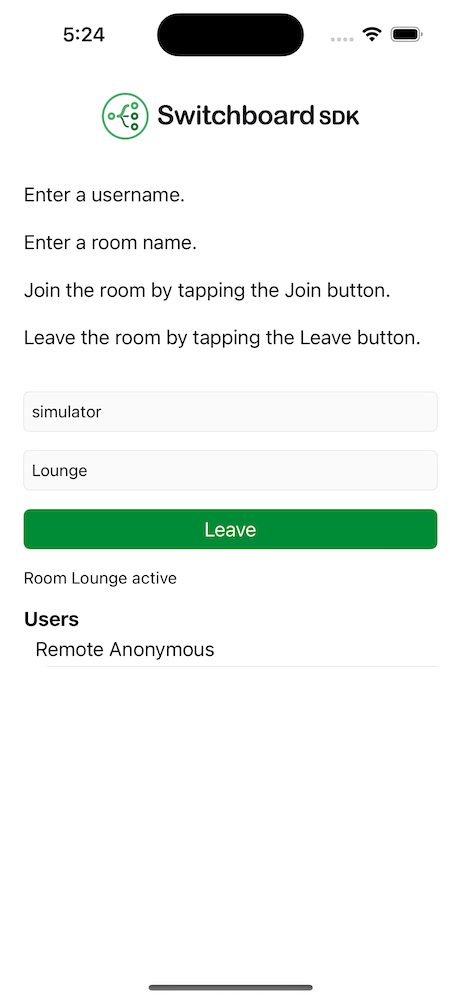
Room Screen
The Room screen consists of a username and room name input field, a join button and a user presence list.
To be able to join a room a username and a room name has to be entered. After joining a room the voice communication is possible with the remote parties in the same room.
Audio Graph
The audio graph for the Room screen looks the following:
The source and sink ResampledNodes are needed to resample the signal from the device sample rate to the communication systems audio bus sample rate. Our microphone input is routed to a sink node for transmission. The source node receives the remote audio and it is routed to the speaker output.
Code Example
- Swift
- Kotlin
import SwitchboardSDK
import SwitchboardAgora
class AudioSystem {
let audioEngine = SBAudioEngine()
let audioGraph = SBAudioGraph()
let multiChannelToMonoNode = SBMultiChannelToMonoNode()
let agoraResampledSourceNode = SBResampledSourceNode()
let agoraResampledSinkNode = SBResampledSinkNode()
let monoToMultiChannelNode = SBMonoToMultiChannelNode()
init(roomManager: RoomManager) {
audioEngine.microphoneEnabled = true
agoraResampledSourceNode.sourceNode = roomManager.sourceNode
agoraResampledSinkNode.sinkNode = roomManager.sinkNode
agoraResampledSourceNode.internalSampleRate = roomManager.audioBus.getSampleRate()
agoraResampledSinkNode.internalSampleRate = roomManager.audioBus.getSampleRate()
audioGraph.addNode(multiChannelToMonoNode)
audioGraph.addNode(agoraResampledSourceNode)
audioGraph.addNode(agoraResampledSinkNode)
audioGraph.addNode(monoToMultiChannelNode)
audioGraph.connect(audioGraph.inputNode, to: multiChannelToMonoNode)
audioGraph.connect(multiChannelToMonoNode, to: agoraResampledSinkNode)
audioGraph.connect(agoraResampledSourceNode, to: monoToMultiChannelNode)
audioGraph.connect(monoToMultiChannelNode, to: audioGraph.outputNode)
}
func start() {
audioEngine.start(audioGraph)
}
func stop() {
audioEngine.stop()
}
}
import com.synervoz.switchboard.sdk.audioengine.AudioEngine
import com.synervoz.switchboard.sdk.audiograph.AudioGraph
import com.synervoz.switchboard.sdk.audiographnodes.MonoToMultiChannelNode
import com.synervoz.switchboard.sdk.audiographnodes.MultiChannelToMonoNode
import com.synervoz.switchboard.sdk.audiographnodes.ResampledSinkNode
import com.synervoz.switchboard.sdk.audiographnodes.ResampledSourceNode
import com.synervoz.switchboardagora.rooms.RoomManager
class AudioSystem(roomManager: RoomManager) {
val audioEngine = AudioEngine(enableInput = true)
val audioGraph = AudioGraph()
val multiChannelToMonoNode = MultiChannelToMonoNode()
val agoraResampledSourceNode = ResampledSourceNode()
val agoraResampledSinkNode = ResampledSinkNode()
val monoToMultiChannelNode = MonoToMultiChannelNode()
init {
agoraResampledSourceNode.setSourceNode(roomManager.sourceNode)
agoraResampledSinkNode.setSinkNode(roomManager.sinkNode)
agoraResampledSourceNode.internalSampleRate = roomManager.getAudioBus().sampleRate
agoraResampledSinkNode.internalSampleRate = roomManager.getAudioBus().sampleRate
audioGraph.addNode(multiChannelToMonoNode)
audioGraph.addNode(agoraResampledSourceNode)
audioGraph.addNode(agoraResampledSinkNode)
audioGraph.addNode(monoToMultiChannelNode)
audioGraph.connect(audioGraph.inputNode, multiChannelToMonoNode)
audioGraph.connect(multiChannelToMonoNode, agoraResampledSinkNode)
audioGraph.connect(agoraResampledSourceNode, monoToMultiChannelNode)
audioGraph.connect(monoToMultiChannelNode, audioGraph.outputNode)
}
fun start() {
audioEngine.start(audioGraph)
}
fun stop() {
audioEngine.stop()
}
fun close() {
audioGraph.close()
audioEngine.close()
multiChannelToMonoNode.close()
agoraResampledSourceNode.close()
agoraResampledSinkNode.close()
monoToMultiChannelNode.close()
}
}
The RoomManager object in the constructor comes from the communication extension. It provides the audio system with the source and sink nodes through which the remote audio can be received and the local audio can be sent.
You can find the source code on the following link:
Voice Communication App - iOS
You can find the source code on the following link:
Voice Communication App - Android